Ever been stumped by a pesky grammar rule? Well, let’s chat about what is a preposition.
You’re writing an email, maybe it’s to your boss or perhaps an old friend. Suddenly you pause — should I end the sentence with ‘to’ or is that even allowed?
The English language can be tricky; filled with rules and exceptions like jigsaw pieces that need to fit just right.
Answering the question “What is a preposition” and knowing how they work in our sentences is akin to mastering the art of driving through traffic lights smoothly without breaking any rules.
Dive into this journey as we explore commonly confused prepositions, crack open some examples, and learn fun ways to remember them for your everyday communication needs.
Table Of Contents:
- What Are Prepositions?
- What Are Prepositional Phrases?
- Functions and Types of Prepositions
- Proper Usage of Prepositions
- FAQs in Relation to What is a Preposition
- Conclusion
What Are Prepositions?
The sixth member of the eight parts of speech is the preposition.
A preposition is a word that indicates the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence, often expressing location, direction, time, or how an action is performed.
Prepositions are a fascinating component of the English language. These tiny words have the power to establish relationships between other elements within a sentence, like connecting nouns or pronouns to verbs.
For instance, consider ‘The dog jumped over the fence.’
Here ‘over’ is acting as our preposition.
A deep dive into understanding prepositions involves appreciating their role in adding context and meaning to sentences. They give us hints about where something happened (like under your bed), when it occurred (before dinner), or how things relate to each other (‘She walked towards him’).
In essence, they act as bridges linking different parts of a sentence together coherently – making them vital for everyday communication.
Their origins trace back to Old English and Middle English times where these position-related terms evolved in usage and form. Many common prepositions we use today like ‘on,’ ‘at,’ and ‘in’ can be traced back hundreds of years.

Source: Your Dictionary
What Are Prepositional Phrases?
Picture this: a preposition, a noun or pronoun, and any modifiers hanging out together. That trio creates the magic known as a prepositional phrase. The preposition is the star; it shows the relationship between the noun or pronoun and the rest of the sentence.
For example, in the sentence “The cat is on the roof,” “on the roof” is the prepositional phrase.
“On” is the preposition, and “the roof” is the object of the preposition.
These phrases can pop up anywhere – at the beginning, middle, or end of a sentence. They’re versatile little language acrobats.
Whether it’s “in the morning,” “under the bridge,” or “with a smile,” prepositional phrases bring details and context to your writing.
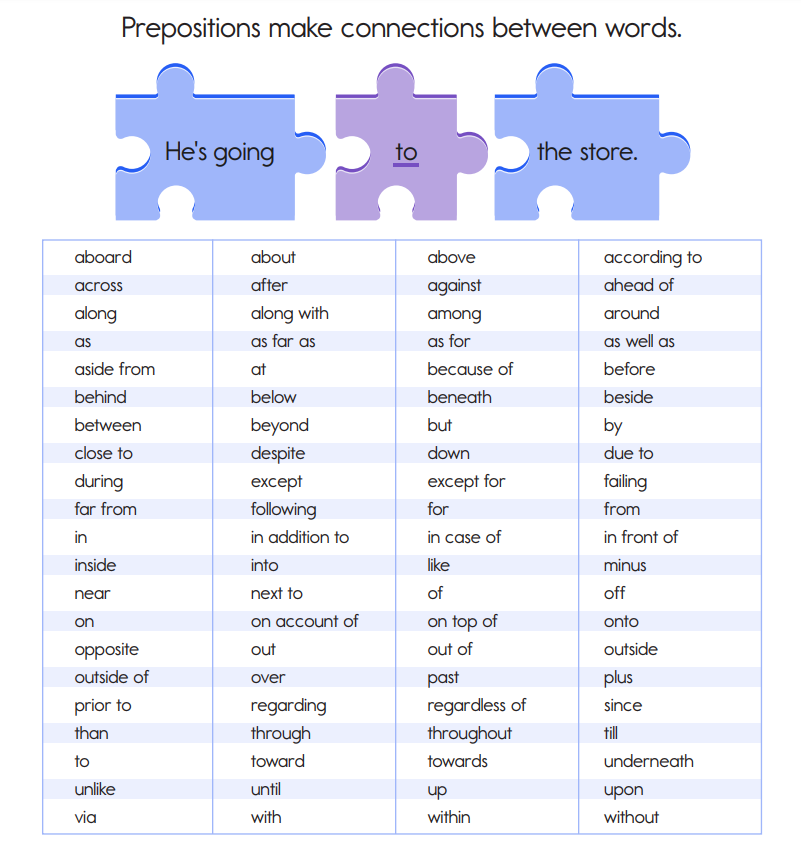
Functions and Types of Prepositions
A preposition’s primary function is to show a relationship between two things — usually expressing direction, place, or time.
Here are some common preposition examples:
- Simple Prepositions: These are your basic prepositions like “on,” “in,” “at,” “by,” and “with.” They’re the foundation of prepositional phrases.
- Compound Prepositions: These are prepositions formed by combining words, like “because of,” “in front of,” or “due to.” They add a bit more detail to your relationships.
- Time Prepositions: These indicate when an action is happening. Think “before,” “after,” “during,” “in,” and “on.” They’re your temporal tour guides.
- Place Prepositions: These prepositions tell you where something is happening. “On,” “under,” “over,” “between,” and “behind” are some classic examples.
- Direction Prepositions: These show movement. “To,” “toward,” “through,” and “across” point you in the right direction.
- Agent Prepositions: These indicate the person or thing responsible for an action. “By” and “with” often play this role.
- Prepositions of Purpose: These explain why something is happening. “For,” “because of,” and “due to” fall into this category.
- Prepositions of Possession: These tell you who owns what. “Of” is a classic player here, as in “house of dreams.”
- Prepositions of Measurement: These give you the specifics. “Inches,” “feet,” “centimeters,” and “miles” help quantify your descriptions.
- Prepositions of Comparison: When you want to compare things, you might use prepositions like “like,” “unlike,” “as,” or “than.”
These little words are the glue that holds our sentences together, quietly doing their job to give your content structure and meaning.
Proper Usage of Prepositions
Confusing prepositions can be difficult to utilize, however, comprehending the regulations makes it much simpler.
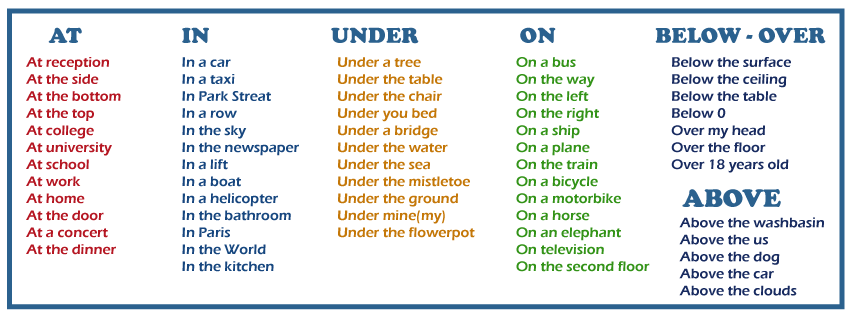
Let’s take “on” and “in” as examples. In English language communication, these are two commonly confused prepositions. Using them correctly helps avoid making mistakes that might lead to misunderstandings.
Let’s start with ‘on’. We often use this when referring to surfaces or specific days. For example: ‘The book is on the table’, or ‘We will meet on Friday’.
‘In’, however, indicates enclosed spaces or nonspecific times during a day, month, or year like in sentences such as ‘I live in New York’ or ‘It happened in August’.
Misusing prepositions is one mistake many writers struggle with. There are ways to get around this problem by using some handy tools online for better understanding and testing your knowledge about the correct usage of prepositions.
Merriam-Webster Dictionary, for instance, provides clear definitions along with sentence examples that can help you grasp how different prepositions function within context.
Source: Java T Point
Examples of Preposition Usage In Context
When it comes to mastering prepositions, examples are your best friends. They give you a clear idea of how these function words work in sentences and help build spatial relationships between objects.
The power of prepositions is truly felt when they’re used with nouns or noun phrases.
Consider this: “The dog jumped over the fence.” Here, ‘over’ is the preposition linking ‘dog’ (the subject) and ‘fence’ (the object).
Prepositions can also indicate place or location.
For instance, “In our home, no one goes hungry.” The word ‘in’, as a common preposition adds meaning to where something happens – our house in this case.
Spatial relationships can be another fascinating use for them too.
Think about waiting “at” traffic lights or sitting “by” the dining table; both scenarios accurately describe physical locations relative to other entities.
A great way around commonly confusing prepositions like ‘at’, ’on’, and ’in’ is by referring back to your style guide.
For example:
‘At’ is used when referring to an exact point or location (“I’m waiting at the bus stop”). ‘On’ refers to a surface (“The book is on the table of contents”). And ‘In’ is used for enclosed spaces (“She’s hiding in her room”).
FAQs – What is a Preposition
What is a preposition and examples?
A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between two parts of a sentence. Examples include “in,” “at,” and “on.”
What’s the deal with phrasal verbs?
These quirky expressions consist of a verb followed by an adverbial particle acting as its object (like “run out” meaning deplete).
Can I end my sentence with a position?
While not always preferred stylistically, ending sentences with a position isn’t grammatically wrong – contrary to what we were taught at school.
What are three examples of sentences using Prepositions?
All these sentences demonstrate the beauty of prepositions in action.
“She left it ON the table,” showcases placement, while “They went TO school early,” points out direction. Solidarity is depicted through “He stood BY his friend during tough times.”
Conclusion
Prepositions may not be as difficult to master as initially thought; the secret lies in diligent practice and perseverance.
So, what did we learn about what is a preposition?
We learned that they’re small but mighty words, guiding our sentences in direction, time, or introducing an object. We discovered the many types of prepositions — from those showing direction like ‘to’ and ‘on’, to ones indicating time such as ‘in’ and ‘at’.
Through examples and resources shared here, you’ve gained insights into using them correctly in your everyday communication.
Your newfound knowledge can be applied at home, the grocery store, or even when writing an email to your boss, it’s all part of becoming more fluent in English grammar.
If you’re not confident with prepositions and prepositional phrases, AI tools can help ensure that you are using them properly. With an AI writer like RankWell, you will never have to worry about preposition mistakes ever again.